Basics of the Terminal
Open the terminal
You can open the terminal by pressing Ctrl + Shift + ` or by clicking on the Terminal tab in the top left bar of VS Code.
Navigating Folders (Directories)
Make a folder/subdirectory
$ mkdir world
Your folders will now look like this on the left side of VS Code:
other-folder1/
other-folder2/
world/
You can also make a folder in the lefthand EXPLORER panel in VS Code as in the image below:
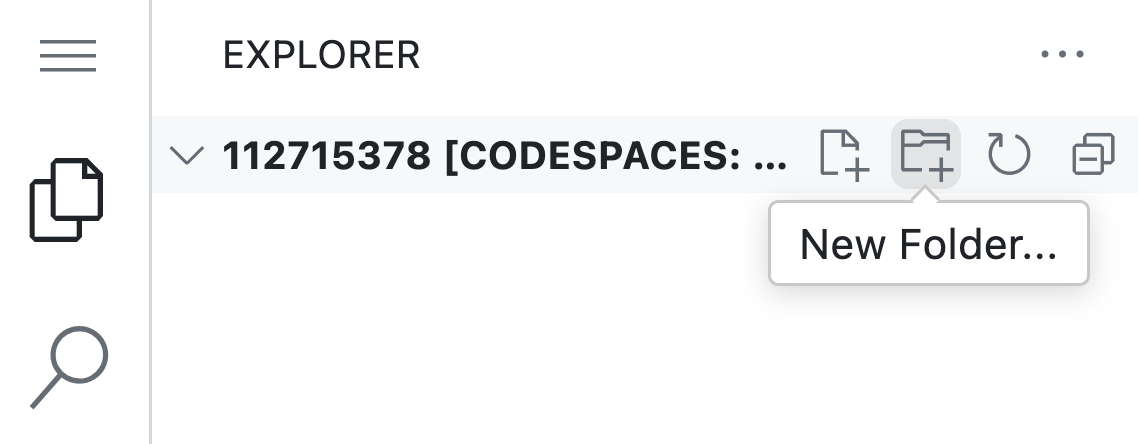
Enter a folder in terminal
$ cd world
You will now be in the world folder:
world/ $
List contents of a folder
$ ls
You will see the contents of the folder:
$ ls
other-folder1/ other-folder2/ world/
$
Exit a folder / go to a higher-level folder
psets/1/ $ cd ..
You will know be in the parent folder psets:
psets/ $
Check the current folder
You can check the current folder by typing:
$ pwd
You will see the current folder (the “present working directory”):
$ pwd
/Users/username/psets/1
$
Files
Create a file
$ code hello.c
You can also create a file in the lefthand EXPLORER panel in VS Code.
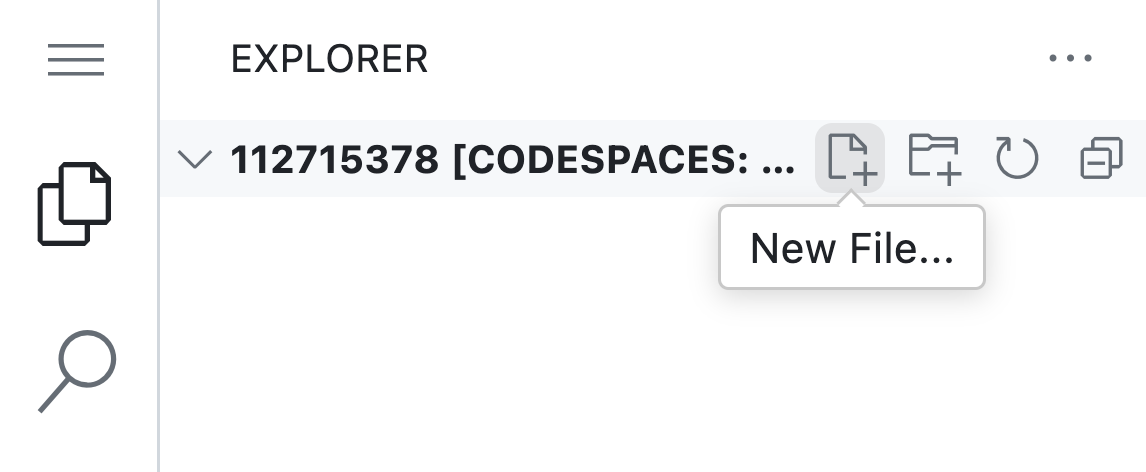
Compile a C file
A C file features human-readable code that needs to be compiled (i.e., translated) into machine-readable code. You can compile a C file like this:
$ make hello
Run a C file
You can run the compiled file like this:
$ ./hello
Delete a file or folder
You can delete a file like this:
$ rm hello.c
You can delete a folder and its contents like this:
$ rm -r world
You can also delete a folder and its contents like this:
$ rm -rf world
What are the differences between these commands?
rm hello.cwill delete the filehello.c.rm -r worldwill delete the folderworldand all its contents recursively.rm -rf worldwill delete the folderworldand all its contents recursively and forcefully, ignoring any errors.
Note that rm -rf is a very dangerous command that will delete everything in the folder and subfolders without asking for confirmation. Be very careful when using this command!